To pristine your lawn pristine, a well-maintained lawn mower is a key helper. At your heart of your mower’s engine lies a small but mighty component, the lawn mower spark plug. This essential part is responsible for creating the spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture, powering your mower. But over time, the spark plug could wear out or become fouled, leading to a range of engine problems. Do you know how to properly change it? In all lawn mower parts, these parts can easily fail; knowing how to replace them is a valuable skill for many lawn mower owners. In this guide, I will walk you through the lawn mower spark plug replacement process, from identifying a faulty plug to installing a new one.
Related Post: How to Change the Oil Filter in a Lawn Mower?
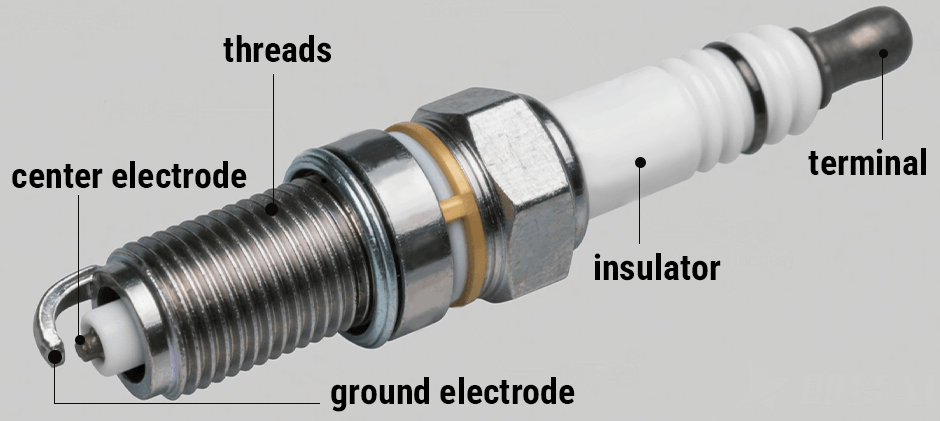
How to Tell Your Lawn Mower Spark Plug is Bad?
Recognizing the signs of a failing spark plug can save you time and frustration. If you’re wondering when to replace a lawn mower spark plug, look out for these common indicators:
- Difficulty Starting: One of the most common symptoms. If your mower cranks but struggles to start, or won’t start at all, a lawn mower spark plug check is a good first step.
- Engine Misfires: The engine may sputter or run unevenly, indicating inconsistent ignition.
- Rough Idling: If the mower shakes excessively or sounds rough when idling, the spark plug could be the culprit.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A worn spark plug can lead to inefficient combustion, causing your mower to use more fuel than usual.
- Reduced Power: You might notice the mower struggling to cut through thick grass or losing power during operation.
- Visible Wear or Damage: A physical inspection can reveal carbon buildup, oil fouling, or a worn electrode.
As a general rule for small engine maintenance, it’s advisable to replace the spark plug at the beginning of each mowing season or after approximately 25-50 hours of use, though some heavy-duty plugs can last longer. Always consult your lawn mower’s operator manual for specific recommendations for your model, whether it’s a Honda, Briggs & Stratton, or Craftsman.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Change a Lawn Mower Spark Plug
Before you begin, gather the following tools and lawn mower parts:
- New Spark Plug: Ensure you have the correct spark plug for your small engine. Check your mower’s manual or the old spark plug for the part number.
- Spark Plug Wrench or Deep Socket Wrench with Ratchet: The size will depend on your specific spark plug. A dedicated lawn mower spark plug removal tool often has a rubber insert to grip the plug.
- Spark Plug Gap Tool/Feeler Gauge: Essential for checking and adjusting the gap on the new plug.
- Gloves: To protect your hands.
- Safety Glasses: To protect your eyes from debris.
- Clean Rag or Brush: For cleaning the area around the spark plug.
- (Optional) Torque Wrench: For precise tightening, if you have the torque specifications.
- (Optional) Anti-seize Compound: To make future removal easier.
Safety First
Working with any engine requires caution. Follow these safety steps:
- Ensure the Engine is Cool: Never work on a hot engine to avoid burns.
- Disconnect the Spark Plug Wire: This is the most crucial safety step. Firmly grasp the boot (the rubber or metal cap covering the spark plug) and pull it off. This prevents accidental starting.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area, especially if you’ve recently run the mower.
- Wear Safety Gear: Put on your gloves and safety glasses.
Now you have the tools and materials you need, and you know how to protect yourself. It is time to change your lawn mower spark plug. It could be a straightforward process. Remember to follow these steps carefully:
Step 1: Locate the Spark Plug
The lawn mower spark plug location is typically on the front or side of the engine, sometimes near the top. It will have a thick black wire (the ignition wire or spark plug lead) connected to its top.
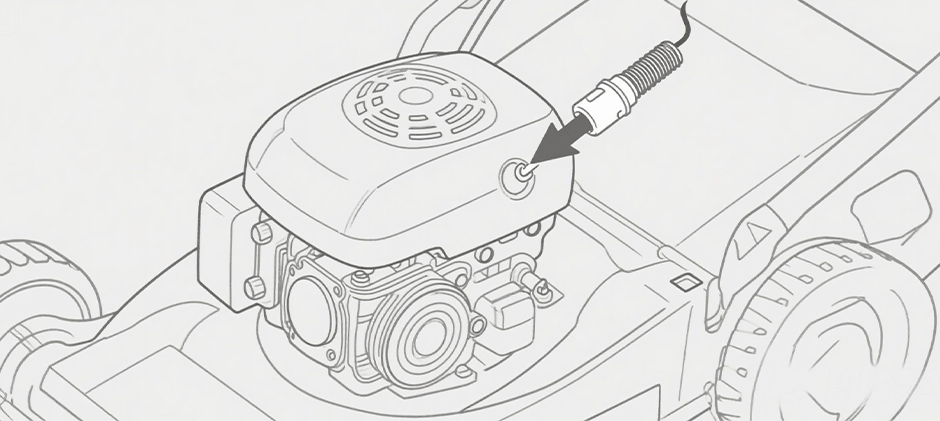
Step 2: Clean the Area Around the Spark Plug
Before removing the old plug, use a clean rag or a brush to wipe away any dirt, grass clippings, or debris from around its base. This prevents anything from falling into the engine cylinder when the plug is removed.
Step 3: Remove the Old Spark Plug
- Ensure the spark plug wire is disconnected.
- Place your spark plug wrench or socket firmly over the spark plug.
- Turn the wrench counterclockwise to loosen and remove the plug. If it’s tight, apply steady pressure. Avoid forcing it, as this could damage the cylinder head threads.
Step 4: Inspect the Old Spark Plug
Once removed, examine the tip of the old spark plug. Its condition can tell you a lot about your engine’s health. This is an important part of engine troubleshooting.
| Appearance of Spark Plug Tip | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Light tan or grey deposits | Normal wear, engine running well. |
| Black, sooty (dry) deposits | Rich fuel mixture, clogged air filter, prolonged idling, incorrect heat range. |
| Oily, wet black deposits | Oil is leaking into the combustion chamber (worn piston rings, valve seals). |
| White, chalky, or blistered | Engine overheating, lean fuel mixture, incorrect spark plug heat range. |
| Worn or eroded center/ground electrode | Normal wear over time, plug is due for replacement. |
| Damaged insulator or bent electrode | Physical damage, possibly from incorrect installation or foreign object. |
Understanding how to tell if a lawn mower spark plug is bad by its appearance helps diagnose underlying issues beyond just a worn plug.
Step 5: Check and Adjust the Gap on the New Spark Plug
Every lawn mower spark plug has a specific gap requirement – the distance between the center electrode and the ground electrode. This gap is crucial for a strong spark.
- Consult your mower’s manual or the spark plug manufacturer’s specifications for the correct lawn mower spark plug gap. Common gaps range from 0.020 to 0.030 inches.
- Use a spark plug gap tool or feeler gauge to measure the gap on your new spark plug.
- If adjustment is needed, gently bend the ground electrode (the curved piece of metal) towards or away from the center electrode using the adjuster on your gap tool. Do not pry against the center electrode, as this can damage it. Re-check the gap until it’s correct.
Step 6: Install the New Spark Plug
- (Optional) Apply a small amount of anti-seize compound to the threads of the new spark plug. This helps prevent it from getting stuck in the future. Be careful not to get any on the electrodes.
- Carefully insert the new spark plug into the cylinder head by hand. Turn it clockwise to thread it in. It should screw in easily for several turns. If you feel resistance, stop immediately – it might be cross-threaded. Unscrew it and try again.
- Once finger-tight, use the spark plug wrench to tighten it further. A common guideline is an additional 1/4 to 1/2 turn for plugs with a gasket, or about 1/16th of a turn for tapered seat plugs once they make contact. If using a torque wrench, tighten to the manufacturer’s specified torque. Over-tightening can damage the plug or the engine’s cylinder head.
Step 7: Reconnect the Spark Plug Wire
Push the spark plug wire boot firmly back onto the terminal end of the new spark plug until you feel or hear it click into place. Ensure it’s secure.
Step 8: Test the Mower
With everything reconnected, try starting your lawn mower. It should start more easily and run more smoothly with the new lawn mower spark plug. If your lawn mower won’t start after a spark plug check and replacement, double-check your connections and ensure you used the correct, properly gapped plug. If problems persist, further ignition system checks or fuel system vs spark plug issues investigation may be needed.

How to Choose the Best Lawn Mower Spark Plug for Your Mower?
Selecting the right lawn mower spark plug is vital. Using an incompatible plug can lead to poor performance or even engine damage.
- Check Your Manual: The owner’s manual for your lawn mower is the best source for the correct spark plug part number.
- Match the Old Plug: If you don’t have the manual, note the numbers and letters on the old spark plug. These codes indicate the plug’s characteristics, such as thread size, reach, and heat range. You can often find a direct replacement or an equivalent from various brands.
- OEM vs. Aftermarket: Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) spark plugs are made by or for your mower’s engine manufacturer (e.g., a spark plug for a Honda lawn mower or a Briggs and Stratton lawn mower spark plug). Aftermarket plugs are made by third-party companies and can be a cost-effective alternative, often offering comparable or even enhanced performance.
- Consider Reputable Brands: Look for well-known spark plug brands that offer quality and reliability.
Many home improvement stores like Home Depot offer spark plugs for lawn mowers, but specialized lawn mower parts suppliers often have a wider selection and expertise.
Conclusion
Changing a lawn mower spark plug is a simple yet effective maintenance task that can significantly improve your mower’s performance and longevity. By following these steps, you can ensure your equipment is ready to tackle your lawn care needs.
If you’re looking for high-quality, affordable aftermarket lawn mower parts, including the best lawn mower spark plug for your specific model, look no further. At Fridayparts, we pride ourselves on our vast inventory and wide compatibility for many heavy equipment brands, including lawn mowers. We understand the importance of reliable parts for your machinery. Visit our website or contact us today to find the perfect lawn mower spark plug and other essential lawn mower parts to keep your equipment running at its best!
