Seeing the Check Engine Light during a job is stressful — especially when you’re far from your workshop. One code that often appears but is widely misunderstood is P0420. It points to the emissions system, but the real cause isn’t always what you think.
This quick guide explains what P0420 means for heavy‑duty off‑road equipment, how serious it is, and what steps you can take to diagnose and fix it without wasting money on unnecessary parts.
What Does Code P0420 Mean
Code P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
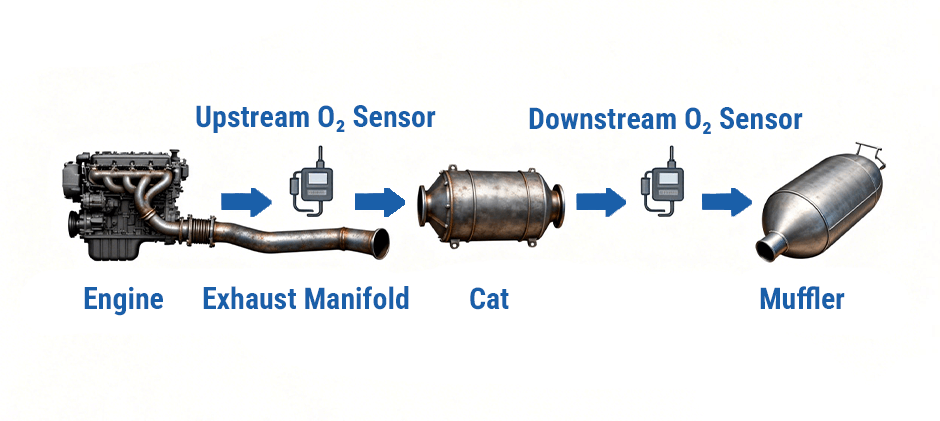
Your machine’s Engine Control Module (ECM) detects that the catalytic converter isn’t cleaning exhaust gases efficiently. It compares two oxygen sensor readings:
- Upstream O₂ Sensor (before converter): Measures raw exhaust — readings fluctuate quickly.
- Downstream O₂ Sensor (after converter): Measures treated exhaust — normally stable.
When both sensors start showing similar patterns, the ECM assumes the converter is failing and triggers code P0420.
“Bank 1” simply means the engine side containing Cylinder #1.
How Serious Is It?
It depends on symptoms:
- Only the Check Engine Light: You can keep operating short-term, but plan diagnostics soon. Continuing too long can eventually damage the converter.
- Reduced power, sluggish performance, or a rotten‑egg smell: Stop using the machine immediately. These signs mean the converter may be clogged or overheating, which can cause severe engine damage.
Common Symptoms
- Check Engine Light on
- Poor power or acceleration, often described as reduced engine power
- Higher fuel use
- Rotten‑egg odor from exhaust
- Failed emissions test
Main Causes of Code P0420
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: A bad downstream O₂ sensor can send false data.
- Exhaust Leaks: Cracks or loose gaskets between sensors can let air in, confusing the ECM.
- Engine Issues: Misfires, rich fuel mixtures, or oil contamination quickly ruin converters.
- Failed Converter: Extreme heat, impact damage, or long‑term contamination can destroy it.
- Excessive Idling: Prolonged idling can cause exhaust temperatures to be too low for the converter to operate effectively, leading to carbon buildup and reduced efficiency.
- Physical Damage: On rough job sites, impacts to the undercarriage or flying debris can directly damage the converter’s housing or its internal ceramic core.
- Poor Fuel Quality: Using low-grade or contaminated fuel, especially in remote areas, can accelerate the aging and failure of oxygen sensors and the catalytic converter.
Step‑by‑Step Diagnosis
1. Scan All Codes: Check for misfires or fuel‑trim errors that could cause P0420.
2. Inspect Exhaust System: Look for visible leaks, cracks, or soot marks.
3. Check Live O₂ Data:
- Upstream sensor = rapid swings
- Downstream sensor = mostly stable
- If both mimic each other, → converter not working.
4. Check Engine Performance: Misfires, leaks, and poor fuel trims all point to upstream issues.
How to Fix Code P0420
Step 1: Try a Converter Cleaner
Add a catalytic converter or exhaust cleaner (like Dura Lube) to your fuel. These products can remove mild carbon buildup and sometimes clear the code. They won’t fix melted or broken parts, but are worth trying first.
Step 2: Repair Root Problems
- Fix exhaust leaks or replace bad gaskets.
- Replace faulty O₂ sensors.
- Correct engine issues causing unburned fuel (spark plugs, injectors, coils).
Step 3: Replace the Converter (Last Resort)
Only do this once all other causes are fixed. Always choose a quality direct‑fit converter rated for your equipment.
Important: Avoid “Spacer Tricks”
Installing spacers to trick the O₂ sensor may temporarily turn off the light — but it hides the problem, can cause more damage, and is often illegal in many areas.
FAQs
Will a fuel additive fix it?
Sometimes. Cleaners can dissolve carbon buildup, but won’t repair leaks or broken parts.
Is it the sensor or the converter?
Analyze live data. If the downstream sensor mimics the upstream, the converter’s bad. If the downstream sensor is lazy or dead, replace the sensor.
Can rough terrain cause this code?
Yes. Vibration or impacts can crack exhaust pipes or damage the converter inside.
How much does it cost to fix?
- Cleaner: ~$30
- Gaskets/Sensors: $50–$300
- Converter: $1,000–$3,000+
Accurate diagnosis saves you from replacing expensive parts unnecessarily. For context, you can compare these costs to other common repairs, like an alternator replacement or a head gasket replacement. Replacing an alternator might cost between $500–$1500, while a head gasket replacement is a major repair that can run $2500–$5000+. Compared to that, prioritizing the diagnosis and replacement of a $150 oxygen sensor is far more cost-effective.
Final Thoughts
Code P0420 means the emissions system isn’t working efficiently — but that doesn’t always mean the converter is bad. Check sensors, leaks, and engine health first.
After a thorough diagnosis, get the exact parts you need to solve the problem for good. Whether your inspection points to a faulty oxygen sensor, a leaking exhaust gasket, or underlying issues like worn spark plugs or a failing fuel injector, FridayParts has the high-quality, direct-fit components to get your machine back to peak performance.
