Modern off-road equipment owners depend on powerful machines built for endurance — but even the most robust Komatsu excavators, dozers, and wheel loaders rely on precise electronic systems that monitor every detail of performance. When an unexpected fault arises, it typically manifests as a diagnostic or fault code. For most operators, these cryptic alphanumeric codes can be confusing.
This in-depth guide will help you decode Komatsu fault codes, understand their technical meaning, and apply real-world solutions. By the end, you’ll be able to identify common issues faster, reduce downtime, and keep your machinery running at full capacity.
What are Komatsu Diagnostic Codes?
Komatsu machines use embedded diagnostic systems that continuously monitor pressure sensors, valves, circuits, and electronic controllers. Each system alert or fault is represented by a Komatsu error code, helping operators locate and interpret machinery problems quickly.
These diagnostic codes typically trigger when the Electronic Control Module (ECM) detects a failure in one of the monitored systems — such as the engine controller, fuel injection sensors, or hydraulic actuators. Each code corresponds to a symptom, for example:
- E-codes (like E02–E20): General equipment system errors (engine, hydraulic, parking brake).
- CA-codes: Engine and sensor-related issues.
- D-codes: Electrical or control circuit faults.
- DW/DX codes: Solenoid and EPC (Electronic Pressure Control) valve failures.
In other words, each code represents an automated message from your machine’s control system, signaling where and what the problem is.
Example: A Komatsu PC200-8 machine showing CA115 indicates an engine speed sensor fault — likely caused by a broken sensor, wiring issue, or connector corrosion.
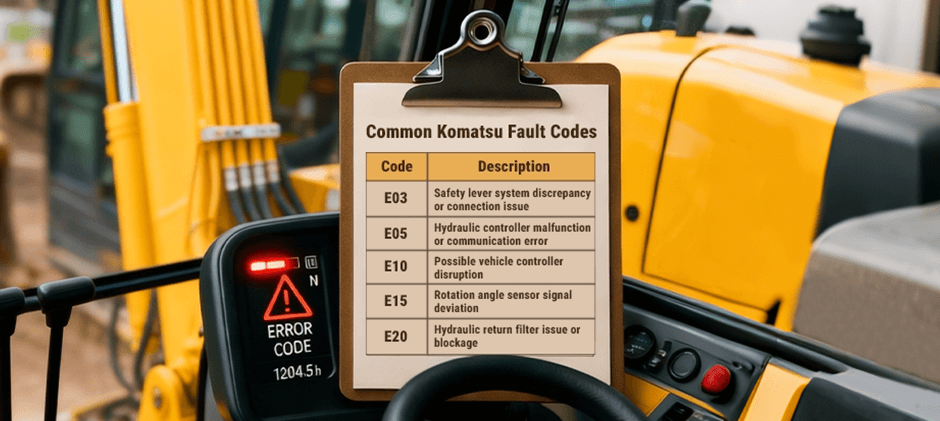
How to Decode Komatsu Fault Codes?
While Komatsu’s diagnostic structure looks complex, every code follows consistent logic. Let’s break it down.
| Code Format | Category | Meaning / System Involved |
|---|---|---|
| E00 – E99 | Equipment / General System | Engine, hydraulic, safety lever, controller errors |
| CA100 – CA999 | Engine & Fuel Sensors | Pressure, temperature, power supply, rail pressure |
| D-code (DA, DW, DX…) | Circuits & Solenoids | Valve, switch, relay, or harness issues |
| B@XXXX | Fluid systems | Hydraulic oil, coolant, or brake temperature alerts |
| 989/AA/AB series | Lockout & Electrical | Power, controller lock, overcharge, or discharge issues |
Step-by-step decoding example:
- E10 → “Engine Controller Power Failure.” → The engine controller or wiring harness needs inspection.
- CA451 → “Common Rail Pressure Sensor Feedback Value Too High.” → Possible malfunction in the rail sensor or actual overpressure condition.
- DW43KB → “Travel Speed Solenoid Valve Short Circuit.” → Electrical short in a travel speed control solenoid.
Once identified, cross-reference these with your equipment model’s manual or an updated Komatsu fault codes list for precise troubleshooting steps.
Common Komatsu Error Codes List & Solutions
Below is a condensed yet comprehensive list of common Komatsu error codes encountered in excavators, dozers, and loaders. They’re grouped by type for faster reference.
Engine and Powertrain Faults
| Code | Description | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| E10 | Engine controller power malfunction | Inspect ECM power connections, fuses, or ground wires |
| E11 | Engine protection—output power reduced | Check coolant temperature, oil pressure, and air filter |
| CA111 | Internal engine controller fault | Replace or reprogram the ECM |
| CA115 | Engine crankshaft speed sensor failure | Replace the speed sensor, and verify the voltage at the pin connector |
| CA234 | Engine overspeed | Verify throttle calibration, engine load cycle, or operator misuse |
| CA441 / CA442 | Battery voltage too low / too high | Replace the alternator or battery; check the voltage regulator |
| CA689 / CA731 | Backup speed sensor or phase abnormality | Replace the corresponding sensor or inspect the sensor gap |
Air and Fuel System Faults
| Code | Description | Suggested Correction |
|---|---|---|
| AA10NX | Air cleaner clogging | Replace the air filter |
| CA122 | Intake air pressure high voltage | Verify the intake pressure sensor and wiring |
| CA123 | Intake air pressure low voltage | Check for a sensor short or an airflow restriction |
| CA153 / CA154 | Intake air temperature sensor error | Replace or test the IAT sensor |
| CA428 / CA429 | Fuel moisture sensor invalid voltage | Ensure a clean fuel supply, and check the moisture sensor harness |
| CA451 / CA452 | Common rail pressure error | Diagnose the fuel rail pressure sensor or pump lines |
| CA553 / CA559 | Fuel pressure high/low | Evaluate fuel pump regulator (IMV/PCV) |
| CA2311 | IMV solenoid valve failure | Replace the IMV solenoid or inspect the wire harness |
Electrical and Sensor Supply Errors
| Code | Error Definition | Action Plan |
|---|---|---|
| CA352 / CA386 | Sensor supply voltage low/high | Check the 5V sensor power line |
| CA187 / CA227 | Power supply voltage is too high | Inspect the alternator and the ECM feed line |
| CA2185 / CA2186 | Throttle plate supply over/undervoltage | Check the throttle motor sensor |
| DA25KP | 5V sensor power is abnormal | Replace the faulty sensor or verify the supply output |
| D862KA | GPS antenna open circuit | Inspect antenna connection on KOMTRAX |
| DA22KK | Pump solenoid low voltage | Check the controller output and connector corrosion |
| D19JKZ | Personal code relay abnormality | Troubleshoot the security system or key module |
Hydraulic and EPC (Electronic Pressure Control) System Faults
| Code | Description | Next Steps |
|---|---|---|
| DGH2KB | The hydraulic oil temperature sensor is short | Replace the temperature sensor |
| DHPAMA / DHPBMA | Front or rear pump pressure sensor abnormality | Swap pump sensors or review hydraulic line blockage |
| DHS3MA / DHS4MA / DHS8MA | Arm, bucket, or boom PPC pressure sensor abnormal | Check the pressure sensor voltage and circuitry |
| DW43KA / DW43KB | Travel speed solenoid open/short | Replace the solenoid valve |
| DW45KA / DW45KB | Swing brake solenoid open/short | Replace the defective solenoid |
| DXA8KA / DXA8KB | Front pump EPC solenoid valve circuit fault | Inspect for wire chafing or shorting |
| DXE5KA / DXE6KB | Pump confluence LS solenoid open/short | Check the harness and replace the damaged solenoid |
Hydraulic sensor and solenoid malfunctions often stem from dirt-contaminated oil, corroded connectors, or overheated hydraulic lines. Periodic sensor validation helps prevent repeated fault occurrences.
Cooling and Overheating Issues
| Code | Meaning | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| B@BCNS | Engine coolant overheating | Check radiator fins, fan belt, and coolant level |
| B@BCZK | Coolant level too low | Fill coolant, inspect for leaks |
| B@HANS | Hydraulic oil overheating | Change hydraulic filter and oil; check cooler fan |
| AB00KE | The charging voltage is too low | Replace the alternator or tighten the belt |
| A570NX | The engine oil filter clogged | Replace filter element |
How to Clear Komatsu Forklift Error Codes?
After diagnosing and repairing the fault, follow these steps to clear codes from a Komatsu forklift’s system memory:
1. Turn the Machine Power Off.
Wait at least 30 seconds to let the ECM power down.
2. Fix the Underlying Issue.
Ensure faulty parts such as sensors, filters, or solenoids are correctly replaced.
3. Access the Dashboard or Diagnostic Panel.
Use the control keys or onboard monitor as per your machine’s model.
4. Enter Maintenance Mode.
Hold both “mode” and “display” buttons while turning the ignition to “ON.” Select “RESET CODES.”
5. Run a System Check.
Restart the machine; any active fault should reappear only if the problem remains unresolved.
Persistent error messages after repair could signal deeper electrical issues or communication errors among ECM modules.

Maintenance Tips to Avoid Fault Codes
Preventive maintenance is the most potent tool for avoiding code-triggered downtime.
- Keep Electrical Connectors Clean: Dust, oil, or water can cause poor grounding and false readings.
- Replace Filters Regularly: Air and fuel filter blockages trigger frequent AA or CA-series codes.
- Inspect Hydraulic Oil: Overheated or contaminated fluid leads to solenoid circuit errors (DW or DX codes).
- Monitor Battery Health: Low or unstable voltage causes cascading ECM and sensor supply faults.
- Run Routine Diagnostics: Many Komatsu models allow you to run self-diagnostics via the dashboard or service laptop before field failures occur.
Choosing Quality Replacement Parts
Most Komatsu error codes result from sensor fatigue, fuel system contamination, or electrical wear — all of which can be prevented with high-quality components.
If you’re maintaining or overhauling off-road machinery like Komatsu excavators, dozers, or wheel loaders, it’s more efficient and affordable to use certified aftermarket replacements engineered to OEM standards.
Explore Komatsu parts for reliable, OEM-quality aftermarket components, including:
- Hydraulic filters and seals
- Fuel injectors and solenoids
- Cooling fans and radiators
- Complete maintenance kits for PC, WA, and D-series machines
FridayParts offers global shipping, excellent pricing, and thousands of verified Komatsu model-compatible parts — perfect for keeping your equipment performing like new.
Finally Words
Komatsu fault codes aren’t just random numbers — they’re diagnostic signposts revealing the exact condition of your machine. By learning to interpret them, you not only fix problems faster but also anticipate future failures before they happen. With a structured troubleshooting approach, access to detailed code lists, and high-quality parts from FridayParts Komatsu parts, every operator can keep their off-road equipment efficient and reliable in the toughest environments.
