No matter how reliable a Cummins diesel engine is, every piece of heavy off-road machinery eventually shows a warning light. Behind that yellow or red indicator lies a diagnostic code — a key, if you know how to read it. This guide is your complete technical reference to decoding SPN FMI code list data and Cummins fault codes for 2025. We’ll cover how to check fault codes, what the most common ones mean, and how to troubleshoot effectively while keeping your fleet performing at full capacity.
Key Takeaways
- Decode the Engine’s Language: This guide breaks down the structure of Cummins fault codes. You’ll learn what SPN (Suspect Parameter Number) and FMI (Failure Mode Identifier) mean, allowing you to pinpoint the exact source of a problem.
- Master Code Retrieval Methods: Learn how to check fault codes using modern electronic diagnostic tools like Cummins INSITE, as well as the traditional “flash code” method for older engines.
- Quickly Identify Common Faults: Get access to a comprehensive Cummins fault code list covering critical systems like aftertreatment (DPF/SCR), fuel, turbocharger, and EGR, helping you fast-track your diagnosis.
- Get Real-World Solutions: Understand the common causes behind recurring codes—such as sensor corrosion or a clogged DPF—and get effective troubleshooting, code reset, and preventive maintenance tips to minimize downtime.
Related Guide: Before you can accurately diagnose a fault or order the right parts, you’ll need to identify your specific engine. Refer to our Cummins Engine Serial Numbers to quickly find your Engine Serial Number (ESN).
How to Check Cummins Fault Codes?
Checking fault codes on modern Cummins engines is straightforward but requires the right tools and method. Here are the most practical approaches:
1. Using an Electronic Diagnostic Scanner
Professional tools such as Cummins INSITE or multi-brand diagnostic scanners read and interpret both OEM-specific and J1939 standard codes. These devices display parameters like sensor voltage, RPM history, injector balance, and, most importantly, the SPN FMI code list generated by the ECM (Electronic Control Module).
Steps:
- Connect the diagnostic port under the dashboard or engine panel.
- Turn the ignition key on (engine off).
- The tool will identify the ECM and retrieve stored codes.
- Each code typically contains:
- MID (Module Identifier) – Which module showed the fault?
- SPN (Suspect Parameter Number) – Which component failed?
- FMI (Failure Mode Identifier) – How it failed.
2. Manual Flash Code Method (Older Models)
For Cummins ISB, ISC, or ISX engines before electronic display systems, technicians can use the dash switch method:
- Hold the diagnostic switch or key while cycling power.
- The Check Engine light blinks a sequence (e.g., two short and three long flashes = Code 23).
Pro Tip: In field conditions without scanners, this flash method remains a dependable way to identify base-level fault info.

The Complete Cummins Fault Code List
Below are some of the most referenced fault codes in modern Cummins engines, from ISX15 and X12 to QSB and L9 series. The first column shows the SPN, followed by the FMI, and a concise description of the issue. Many of these stem from electronic fuel and emission systems found on off-road equipment like loaders, scrapers, and excavators.
Engine Oil & Pressure System Codes
| SPN | FMI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1 / 18 | Engine Oil Rifle Pressure – Below Normal or Moderately Low |
| 175 | 3 / 16 | Engine Oil Temperature – Voltage High or Above Operating Range |
| 168 | 4 / 16 | Battery Voltage – Below Normal or Above Normal Voltage |
| 167 | 18 | Charging System Voltage – Below Normal |
| 105 | 15 / 16 / 18 | Intake Manifold Temperature – Data Out of Range |
| 111 | 17 | Coolant Level – Low (Least Severe) |
These readings often appear when the oil sensor becomes contaminated or after long idle periods in dusty conditions.
Air & Turbocharger System Codes
| SPN | FMI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 102 | 10 / 15 / 18 | Intake Manifold Pressure – Abnormal Rate or Out of Range |
| 103 | 15 / 18 | Turbocharger Speed – Above or Below Range |
| 641 | 7 / 31 | Variable Geometry Turbo (VGT) Actuator – Mechanical or Control Fault |
| 1209 | 3 / 18 | Exhaust Gas Pressure – Electrical or Pressure Variation |
| 1176 | 18 | Turbo Compressor Pressure – Below Normal Range |
“SPN 641 FMI 7” is one of the top failure alerts in heavy equipment with electronically actuated VGT turbos—usually caused by corroded electrical terminals or soot interference.
Fuel and Injector System Codes
| SPN | FMI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 157 | 7 / 16 / 18 | Injector Metering Rail Pressure – Faulty or Outside Range |
| 251 | 10 | Real-Time Clock – Abnormal Rate of Change |
| 1349 | 3 / 4 | Fuel Pressure Sensor Circuit – Voltage Deviations |
| 3480 | 2 / 4 | EGR Valve Position or Fuel Pressure Irregularities |
| 2791 | 5 / 6 / 7 | EGR Valve Control – Open, Ground Short, or Mechanical Error |
These codes frequently originate from low fuel supply pressure, air intrusion in the system, or outdated ECM calibration files.
Aftertreatment System & DEF-Related Codes
Given stricter emissions regulations, the SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) and DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) systems are key in off-road compliance.
| SPN | FMI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1761 | 9 / 18 | DEF Tank Level – Abnormal Data or Low Reading |
| 3242 | 15 / 16 | DPF Intake Temperature – Above Normal |
| 3246 | 15 / 16 | DPF Outlet Temperature – Above Range |
| 3251 | 0 / 15 / 16 | DPF Differential Pressure – Abnormal Reading |
| 3364 | 9 / 13 / 18 | DEF Quality Sensor – Abnormal Update or Drifted Value |
| 4364 | 18 / 31 | SCR Efficiency – Below Normal or Condition Exists |
| 5246 | 0 / 16 | SCR Operator Inducement – Most Severe Limited Torque |
| 3712 | 17 | SCR Warmup/Operator Alert Active |
These faults often trigger engine derate modes to prevent emissions violations. When dealing with SPN 3251 FMI 10, inspect DPF pressure tubing and differential sensors; replacing them with reliable aftermarket parts, such as those from Cummins engine parts, restores compliance faster.
Electrical and ECM System Codes
| SPN | FMI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 343 | 12 | ECM Warning – Internal Hardware Fault |
| 629 / 630 | 12 | Calibration Memory Failure |
| 3868 | 9 | DEF Quality Update Rate – Abnormal |
| 639 | 9 | CAN/J1939 Network – Communication Timeout |
| 3597 | 2 / 18 | Power Supply Lost or Below Normal Voltage |
| 6655 | 4 | ECU Power Lamp – Voltage Below Normal |
Cooling and EGR Temperature Codes
| SPN | FMI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2962 | 16 | EGR Temperature – Above Normal Moderately Severe |
| 411 | 4 / 7 | EGR Differential Pressure – Mechanical Issue |
| 412 | 3 / 16 | EGR Temperature Sensor – High or Overheated |
| 110 | 0 / 15 / 18 | Engine Coolant Temperature – High or Low |
| 4334 | 16 / 18 | DEF Pressure – High or Low Pressure Level |
Cummins Fault Codes Explained
Understanding how to read a Cummins fault code is one of the most important diagnostic skills for off-road machinery maintenance. Each fault code displayed by the ECM (Engine Control Module) contains a set of standardized identifiers, which tell us what went wrong, where, and how serious it is.
Let’s break down the structure using the example shown in the image above: Fault Code: SPN 102 FMI 4 (123)
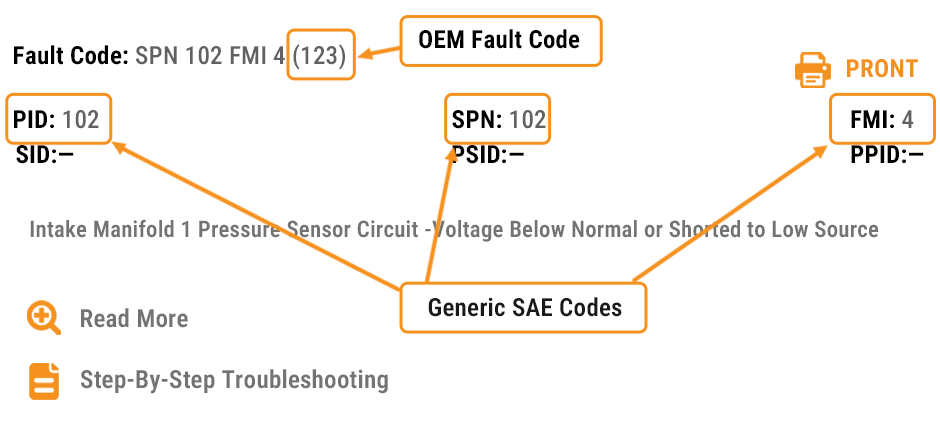
This line actually combines both OEM-specific and SAE J1939 generic codes. Here’s what each part means:
| Code Element | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SPN (Suspect Parameter Number) | 102 | Identifies the specific system or sensor component. SPN 102 refers to the Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor. |
| FMI (Failure Mode Identifier) | 4 | Explains how the fault occurred. FMI 4 means “Voltage Below Normal or Shorted to Low Source.” |
| PID / SID | 102 / — | Shows the data parameter or subsystem (PID = Parameter ID). In this case, it confirms the affected signal channel. |
| OEM Fault Code (123) | Cummins internal reference | Unique to Cummins diagnostic systems and used for service documentation and advanced troubleshooting. |
Popular Cummins Fault Codes
Some codes appear across multiple engine families. Here are the top issues seen across ISX15, QSB6.7, and X12 engines:
| Fault Code | SPN | FMI | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6255 | 1569 | 15 | Engine Protection Derate – Reduced Power |
| 4677 | 1761 | 9 | DEF Tank Level – Abnormal Update Rate |
| 3364 | 9 | — | DEF Quality Signal Drift |
| 2579 | 641 | 7 | Turbo VGT Actuator Mechanical Fault |
| 2962 | 16 | — | EGR Temperature Above Normal |
| 486 | 157 | 16 | Injector Pressure Low |
| 343 | — | — | ECU Hardware Warning |
| 2372 | 95 | 16 | Fuel Filter Restriction – Moderately High |
| 3712 | 5246 | 0 | SCR Operator Inducement Active |
| 639 | 9 | — | J1939 Data Link Timeout |
“Engine Derate” codes like 6255 or 1569 are protective responses. The control system limits torque output to reduce damage risk. Correcting the root fault automatically clears the derate without resetting the ECM.
Common Causes, Real Fixes
- Sensor Wiring Corrosion: In wet environments, sensors along the DEF line or intake system rust or lose ground, causing FMI 4 or FMI 18.
- Contaminated Fuel: Leads to abnormal rail pressure changes (SPN 157 series).
- DPF Ash Accumulation: Causes SPN 3251 FMI 16 or SPN 3720 FMI 15, often resolved after manual regeneration.
- Low Battery Voltage: Triggers network communication codes such as SPN 639 FMI 9.
Tips: About 60% of recurrent Cummins ECM faults link to low-voltage events. Stable power saves sensors—and sanity.”
At this maintenance stage, replacing failing sensors, actuators, and filters with reliable third-party products can save significant time and money. You can explore tested and OEM-compatible Cummins engine parts from FridayParts — including injectors, solenoids, and pressure modules, all with verified aftermarket specifications.
How to Reset Fault Codes?
After repairs, clearing trouble codes ensures your ECM runs current sensor data only. Use your diagnostic tool’s “Clear Faults” function, or for older models, disconnect the battery for several minutes. Always verify that the root cause is fixed before erasing — clearing without repair may hide persistent data.
Preventive Tips for Fewer Fault Codes
- Monitor Data Frequently: Review live pressure and temperature readings rather than waiting for warnings.
- Perform Timely Filter Changes: Follow Cummins-recommended hours for oil, fuel, and DEF filter replacements.
- Keep Electrical Connections Dry: Apply dielectric grease to prevent voltage drop codes.
- Run Weekly Engine Regeneration Cycles: Helps prevent DPF buildup-related SPN 3251 or SPN 3720 codes.
- Use Quality Aftermarket Components: Low-grade sensors may trigger false ECM alerts within days.
Conclusion
Knowing your SPN FMI code list gives you control over what the engine tries to tell you — long before costly failure occurs. Cummins engines support deep diagnostics, enabling fleet managers and mechanics to react fast. When sensor or actuator replacement becomes necessary, turn to Cummins engine parts at FridayParts — trusted OEM-quality components with fast global shipping, high compatibility, and fair pricing. Upgrading your parts today keeps your off-road machinery running efficiently tomorrow.
